B. Wastewater – Capacity Template and Reuse – Spray Irrigation
Wastewater Capacity Template
1. Identify future growth to be served by WWTPs: # of EDUs
2. Identify Service Areas:
Planned Service:
Existing or 3-to-5 year planned service - # EDUs
10-year service - #EDUs
No-Planned Service Area -#EDUs – Need W/S Plan amendment
3. Identify WWTPs: 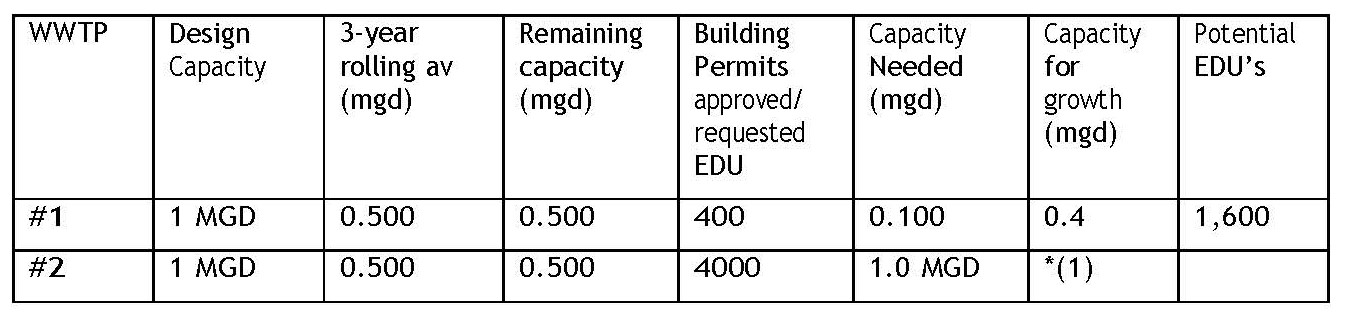
Example table- Refer to the tables provided in the Capacity Management Plans for greater detail
4. Compute Nutrient Loads:
Major Plants (0.5 mgd or greater):
Total Nitrogen: FLOW (mgd) x 4.0 (mg/l) x 8.334 x 365 days/yr
Total Phosphorus: FLOW (mgd) x 0.3 (mg/l) x 8.334 x 365 days/yr
Minor Plants (less than 0.5 mgd):
Total Nitrogen: FLOW (mgd) x 18.0 (mg/l) x 8.334 x 365 days/yr
Total Phosphorus: FLOW (mgd) x 3.0 – 6.0 (mg/l) x 8.334 x 365 days/yr
5. For new plants, or plants that expand beyond their nutrient cap or other limitation, develop plans for expansion or offsets considering current requirements, laws, and information from state agencies:
Identify potential limitations:
a. TMDL
b. Load Cap
c. Compliance issues, including Combined Sewer Overflows (CSOs)/Sanitary Sewer Overflows (SSOs)
d. NPDES requirements
e. Water Supply and Wastewater Capacity Management Plans
f. Inflow/Infiltration
Develop a plan of action:
a. Upgrade WWTPs
b. Plan expansion (amend Water and Sewer Plan)
c. Identify offsets
d. Limit # of EDUs to be developed
e. Water Supply and Wastewater Capacity Management Plans
Update Comp Plan to reflect planned actions
Wastewater Reuse – Spray Irrigation
Option A - Preliminary Spray Irrigation Site Capacity Estimate
Table 2. Estimates of application rates and site capacities based on soil drainage
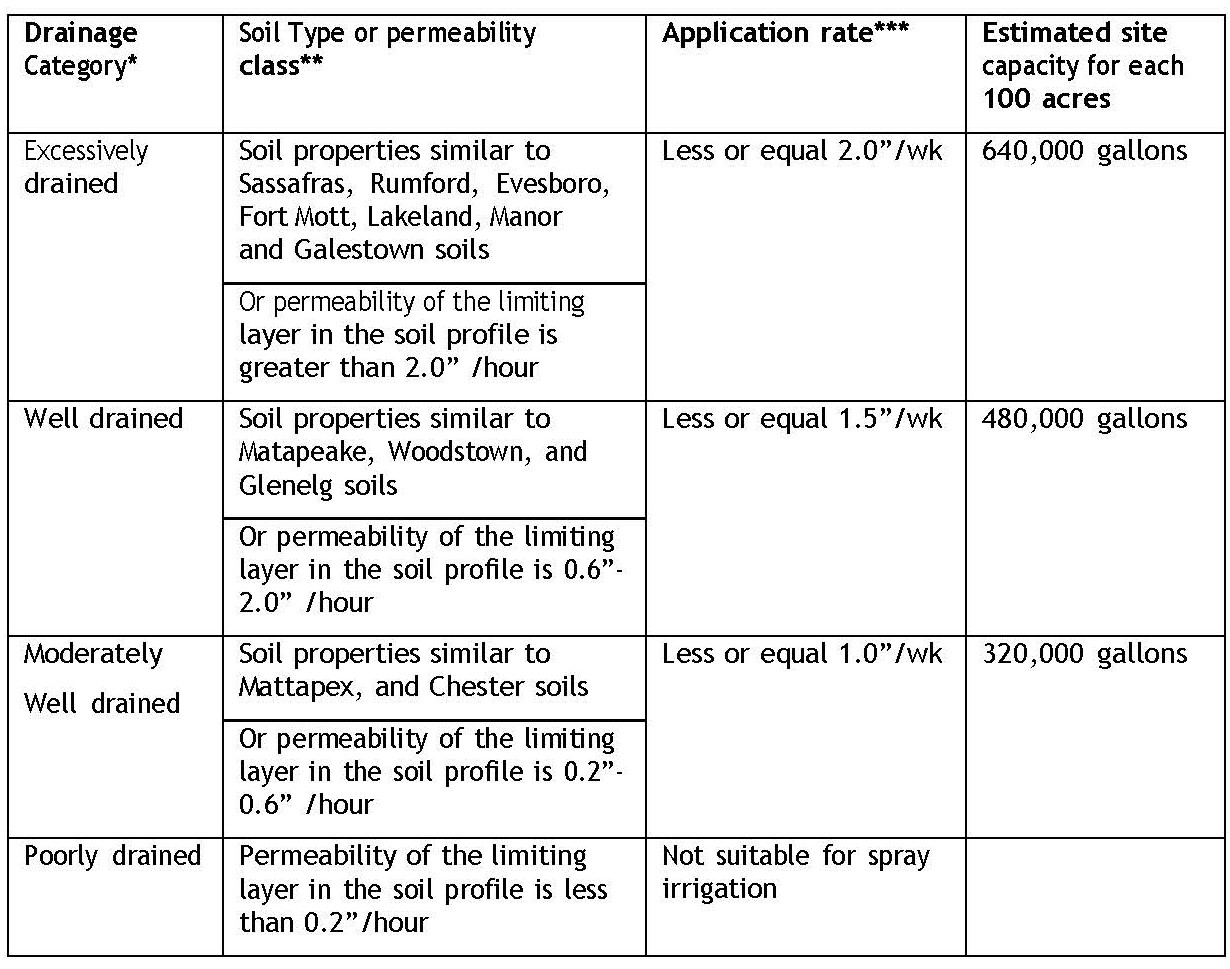
* Soil drainage characteristics can be found in the “General Soil Map” provided in each County Soil Survey
** Soil type and soil permeability can be found in the soil map and soil property table provided in each County Soil Survey
*** Application rates shown in this table are for County planning purposes only and are not to be used for permit applications and system designs.
Option B - Refined Spray Irrigation Site Capacity Estimate
- Determine soil type, soil permeability, land slope, depth to bedrock and ground water table depth from County Soil Survey.
- Eliminate area with slope in excess of 15% in open field and 25% in wooded area.
- Eliminate area with ground water table less than 4 ft or less than 2 ft in Eastern Shore.
- Eliminate area with depth to bedrock less than 4 ft.
- Eliminate area with the most limiting layer soil permeability of less than 0.2”/hr shown in the County Soil Survey.
- Delineate the suitable area (keep 100 ft. away from streams and 25 ft to home structures) and measure the acreage.
- Use Table 2 in Option A to determine the application rate (H) based on the soil type and Equation 1 below to determine the initial site capacity (Q).
- Reduce site capacity by 25% for reserve purpose and determine the final site capacity, Qf (Qf =75% Q).
- Add up final site capacities (Qf) determined from Step 8 for all suitable lands with various soil types in the county.
Equation and Example
Q = [A x 27,154 x (365 –G) x H] / [365 x (E+F)] (1)
Where:
A is area in acres (from Step 6 above)
Q is the flow in gallons per day
E+F is the loading cycle (loading plus rest periods) in days per week
E is the loading period in days per week
F is the rest period in days per week
G is the storage requirement in days per year (90 days for Washington, Allegany and Garrett Counties, 60 days for other counties)
H is the application rate (loading rate) in inches per week Conversion factors:
365 = days per year
27,154 = gallons per acre-inch
The following example of these calculations assumes 100 acres suitable spray irrigation area at 1”/week application rate and a 60-day storage time:
Q = [100 x 27,154 x (365 –60) x 1”/wk] / [365 x (7 days)] = 324,147 gal/day